Miért rossz, ha a hangszóró impedanciája túl alacsony? Kérdésére válaszolva
Zavarba ejtő lehet, amikor az impedanciáról, ohmokról és az autós vagy otthoni hangszórókról beszélünk. Igen, a legtöbb ember ismeri a hangszórókat, az Ohm-besorolást és egyebeket… de mit is jelent ez valójában?
Pontosan miért rossz, ha a hangszóró impedanciája túl alacsony? Erre itt válaszolok, és egyszer s mindenkorra tisztázom.
Ebben a cikkben mindent megtudok, amit tudnia kell:
- Mi pontosan az hangszóró impedanciája?
- Két fő ok, amiért a hangszóró alacsony impedanciája rossz lehet… és miért számít?
- Miért megteheti? használjon nagyobb impedanciájú hangszórókat, de ne alacsonyabbak (és mire számíthatunk)
Sok mindenről van szó, úgyhogy ugorjunk azonnal!
Mit jelent az impedancia a hangszórók számára? Hangszóró Ohm elmagyarázta
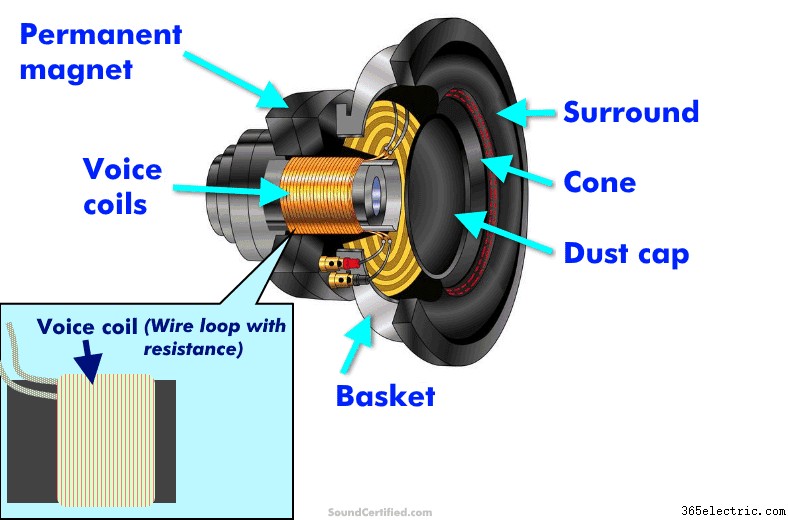
A hangszórót alkotó részek illusztrált képe, beleértve a hangtekercset is. A hangtekercs egy szorosan feltekercselt, hosszú huzal, amely bizonyos mértékű ellenállással rendelkezik a használt elektromos vezetőtől. Mágneses mezőket hoz létre, amelyek előre és hátra hajtják a hangszórókúpot, így hangot kelt, miközben mozgatja a levegőt.
Az elektromosság és az elektronika világában szükségünk van néhány dologra a hasznos munkához:
- Egy feszültséggel ellátott áramforrás az elektromos áram átvezetésére az ellenálláson, motoron stb., hogy valami hasznosat tegyen. Egy otthoni vagy autós erősítő vagy rádió biztosítja ezt.
- Elektromos vezetők (hangszóró vezeték) az áram áramlásához
- Bizonyos szintű ellenállás korlátozni, hogy mekkora áram folyhat (a túl nagy áram hatására a dolgok kiégnek, felforrósodnak stb.)
Ugyanezen alapon, csakúgy, mint a többi elektromos készülék, a hangszórók is olyanok, mint egy kis motor, amelyek áramot használnak, hogy a mozgást (a kúpot) hanggá alakítsák – lényegében ez az összes hangszóró!
Mit jelent a hangszóró impedanciája?
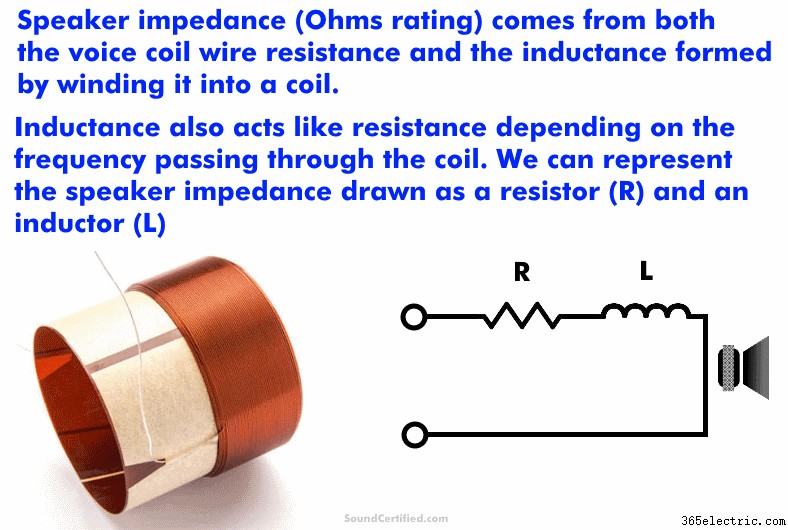
A hangsugárzó impedanciája, az ellenállás Ohm-nak nevezett egységeiben mérve, a teljes a hangszóró ellenállásának mértéke az elektromos áram áramlásával szemben.
A hangszóró impedanciája két dologból adódik:
- A hangtekercset alkotó huzal hosszú tekercsének ellenállása
- Egy speciális tulajdonság, amely akkor jön létre, amikor a vezetéket egy induktivitás nevű tekercsbe tekerik
Csakúgy, mint az akkumulátorban nem lehet rövidzárlat, egy erősítőnek vagy sztereónak is szüksége van néhányra a hangszóró ellenállásának mértéke, hogy korlátozza, mekkora elektromos áramot próbál a rádió vagy az erősítő szolgáltatni.
A hangszórók hangtekercsei nagyon hosszú vezetéket használnak, amely szorosan a hangtekercsbe van tekercselve, amely szükséges a mágneses mezők létrehozásához a kúp mozgásának létrehozásához. E hosszúság miatt mindig van egy bizonyos mértékű ellenállás, amely a hangszóró impedanciájának részét képezi.
Egy adott hangszóró ellenállása szinte mindig néhány ellenállási egység Ohmban mérve.
Mit jelent az induktivitás? Miért számít ez a hangszórók
ban
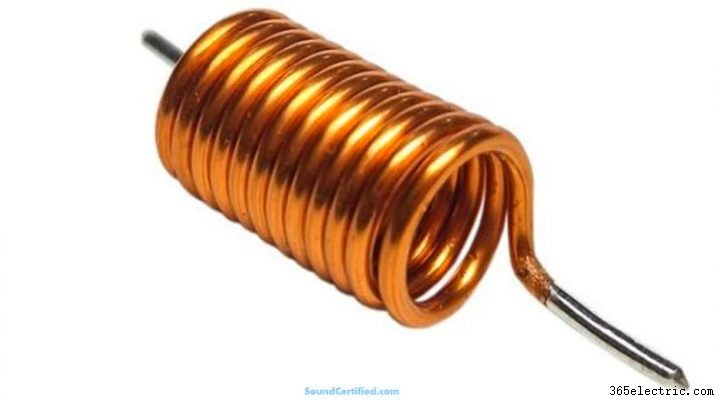

Az induktorok nagyon hasznos elektromos alkatrészek, amelyek kihasználják az induktivitás előnyeit. Az induktivitás a huzalhurokon átáramló elektronok és az emiatt kialakuló mágneses mezők tulajdonsága. Hasonlóan, a hangszóróknak is van induktivitása a hangtekercseik miatt, bár csekély mértékben.
A huzaltekercseknek van egy érdekes mellékhatása, amely az egyenes huzalszakaszokkal ellentétben történik. A hangtekercs huzaltekercse egy hurkot képez, amelynek elektromos tulajdonsága az induktivitás. Ha váltakozó frekvenciát, például zenei jelet alkalmaznak egy induktivitású tekercsre, a jelenlévő mágneses mezők miatt az elektromos áram áramlása ellentétes.
Ezt induktív reaktanciának nevezik, és különbözik az ellenállástól, mivel a frekvencia változásával változik; az ellenállás változatlan marad.
A hangszórók esetében ez számít, mert ez azt jelenti, hogy a összesen Az ellenállás az általam említett két dologból tevődik össze:a huzalellenállásból és az induktív reaktanciából. Az összeg leírására használt név impedancia.
A hangszórók esetében ez azt jelenti, hogy az impedancia (a teljes ellenállás) enyhén változik a zene lejátszásakor a változó hangfrekvenciák miatt. A jó hír azonban az, hogy a hangszórókat továbbra is kategorizálhatjuk Ohm-besorolás szerint, mivel ez mindig elég közel van.
Amikor a hangsugárzók impedanciájáról beszélünk, az emberek legtöbbször a hangsugárzó kategóriákhoz (például 2 ohm, 4 ohm, 8 ohm stb.) rendelt tartományára gondolnak. Így illesztjük a hangszórókat autós vagy otthoni erősítőhöz, rádióhoz stb.
Az elektromos világban az Ohmban mért ellenállás mértékegységei a görög Omega szimbólumként vagy „Ω”ként írhatók fel.Hogyan működik a hangszóró impedancia?
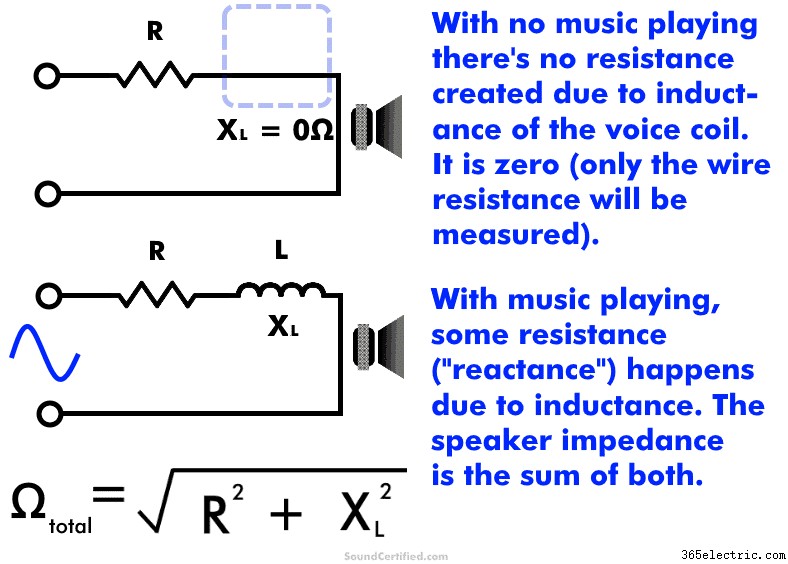
Amikor egy (váltakozó áramból álló) zenei jelet adunk a hangszóróra, az mágneses mezőket hoz létre, miközben az áram átfolyik a szorosan feltekert huzaltekercsen. Érdekes módon egy huzaltekercs olyan mágneses mezőket fejleszt ki, amelyek ellenállnak az áram áramlásának (ellenállás, más néven reaktancia ebben az esetben).
Hasonlóképpen, sok más elektromos alkatrész, például a motorok ugyanolyan elektromos ellenállással rendelkeznek, mint a váltakozó áram (AC) alkalmazása.
How the math works (yeah, it’s a little complicated!)
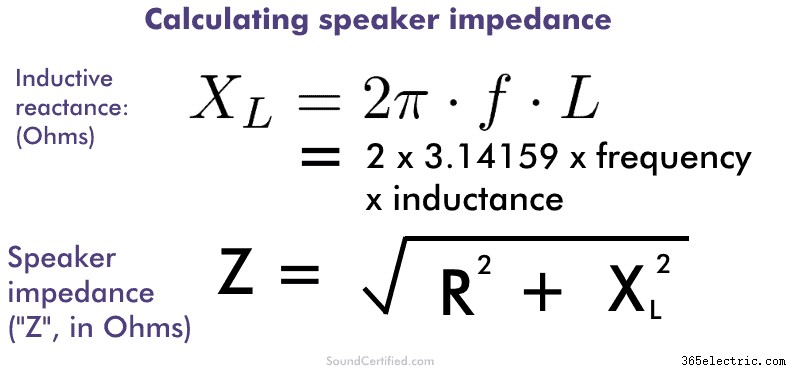
Because of how inductance works and the physics involved, the speaker “impedance” (total resistance) isn’t the sum of the resistance and the inductive reactance. Instead it’s the “algebraic” sum, meaning it’s the square root of the sum of the squares. You may remember this kind of math from trigonometry class.
Speaker impedance isn’t as simple as just adding the measured DC resistance of the coil wire and the inductive reactance for a given frequency.
Instead, speaker impedance is found from the algebraic sum of the coil’s wire resistance and inductive reactance. You can find this by squaring each and then taking the square root of the two numbers added together.
Az induktív reaktanciát általában „Xl”-nek írják, „X sub L”-nek ejtve, és ohm egységekben mérik, mint az ellenállást. Az induktivitás mérése a „Henrie”-nek nevezett mértékegység segítségével történik, és általában „H”-val jelölik:„uH” a microHenries, „mH” a milliHendries és így tovább.
There’s also a corresponding value for capacitors called capacitive reactance (Xc) but that doesn’t usually apply for speaker voice coils. It’s very important for speaker crossovers, however.
Why is it bad if speaker impedance is too low?
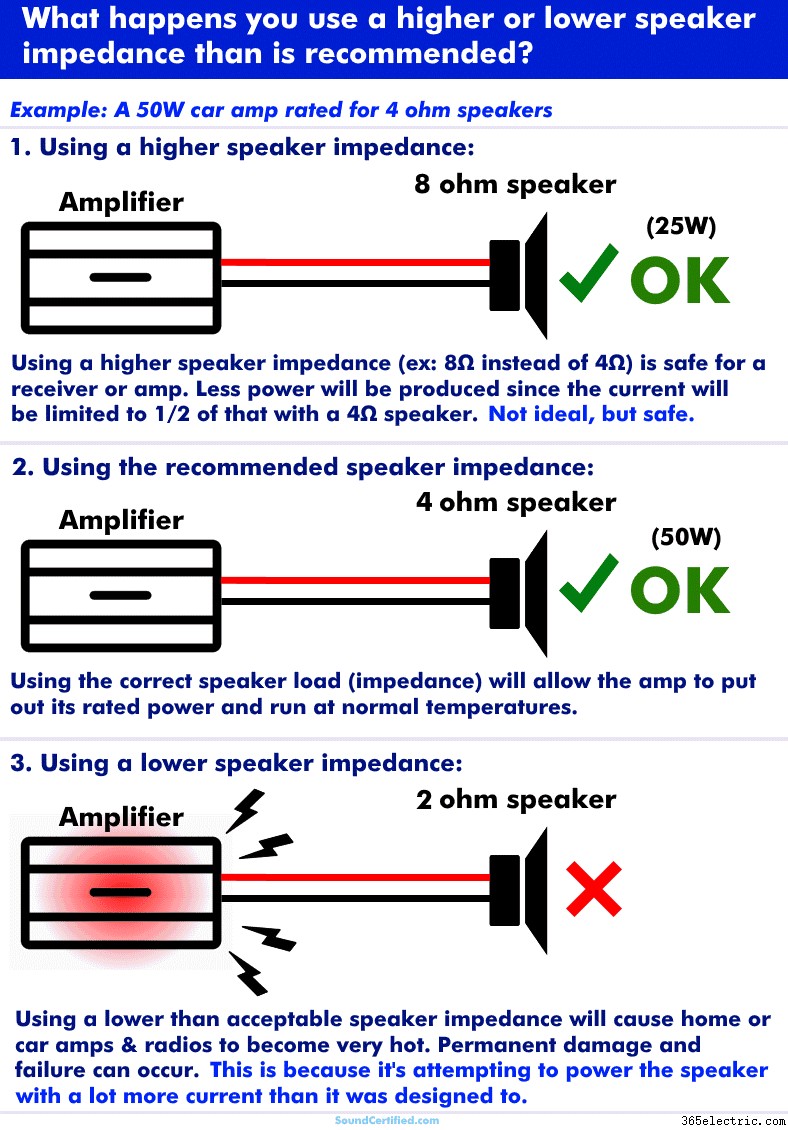
Just like any other device connected to an electrical power source, the speaker impedance will determine how much or how little current a home or car receiver, amplifier, etc will produce. The speaker impedance also affects how some speaker components such as speaker crossovers behave too.
What happens if speaker impedance is too low?
You can connect a higher speaker impedance in most cases without any problems (at least not major ones). A radio, home or car amplifier, etc will still produce sound and run at normal or low temperatures. That’s because a speaker with a higher impedance than expected will reduce how much electrical current the audio source tries to produce.
As a side effect, you’ll get sound but with much lower power output than you would with the correct speaker load. Car stereos or amps, for example, have to work with lower voltages than home stereos so they need a lower impedance 4 ohm speaker typically to produce more power.
Home stereos, on the other hand, have higher voltage available and can use a higher speaker impedance (8 ohms, typically).
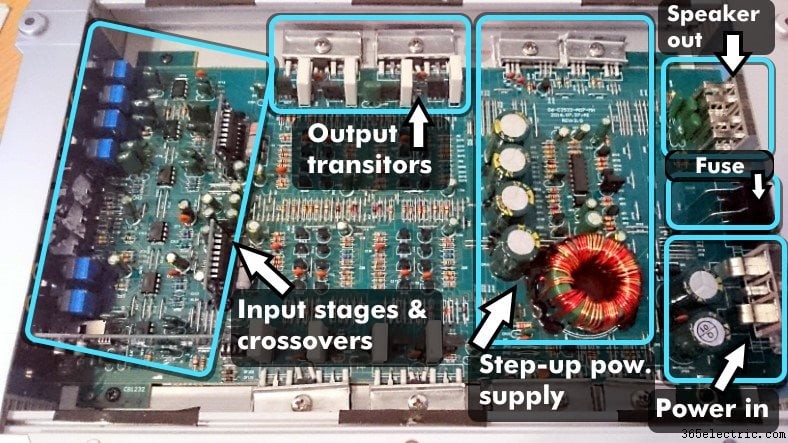
Internal view of an amplifier. When connected to a speaker impedance load that’s too low, the amp will begin to get very hot and this can burn out the output transistors as they can’t handle the heat caused by trying to supply excessive current to a lower speaker load.
However, using a lower speaker impedance is bad because it causes the radio or amp to attempt to put out twice as much (or more!) current than it’s designed for. Your home or car stereo will get very hot quickly and if you’re lucky will go into a self-protect mode and shut itself off.
However, in my experience, it’s pretty common for the output stage electronics to burn out when connected to a lower speaker load than they should be. The high-power transistors in a home or car amplifier or stereo are only rated for a certain amount of heat &electrical current.
When they’re forced to try and handle an amount outside that range they become super hot and start to break down permanently. It doesn’t take long before the damage is permanent and they no longer produce sound.
Caution! Never wire speakers in a way that gives a total speaker load lower than the radio or amp is rated for. Also, don’t guess about the correct speaker impedance – check first.I’ve seen cases where someone’s “friend who’s smart” has as a way to “get more power” but caused a stereo or amp to try to and put out more power than it was designed for. The end result was a burned-out amplifier.
Why does speaker impedance matter for crossovers?
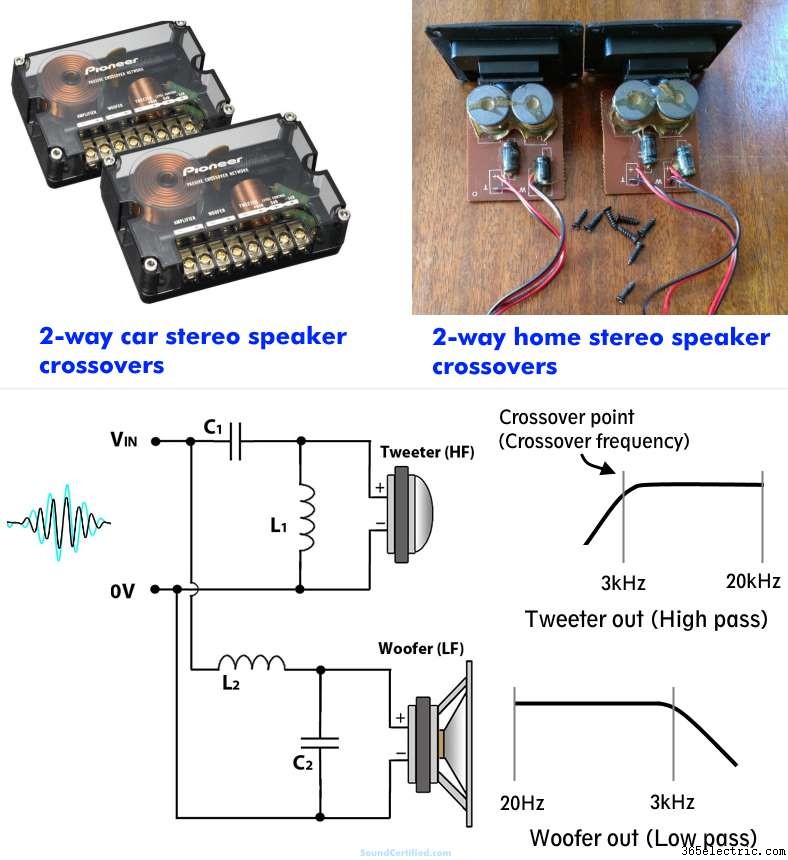
Speaker crossovers work to separate the sound sent to certain speakers for improved sound, reducing distortion, and to give you more control over how they’re used. For example, they block bass that tweeters can’t produce and highs that a woofer can’t produce well. However, they’re designed for a specific speaker impedance. Changing the speaker impedance affects the sound.
Speaker crossovers are amazingly helpful for getting better sound with speakers. Even the cheapest, most basic capacitor connected inline with a tweeter working as a high-pass filter makes a big difference in the sound.
The result is cleaner sound and avoiding possibly damaging it when bass sounds are played.
The catch is that because of how crossover components (capacitors and inductors) behave, they’re designed for specific speaker loads and can’t be used with other Ohm loads without affecting the sound output.
Crossover shift when using different impedance speakers
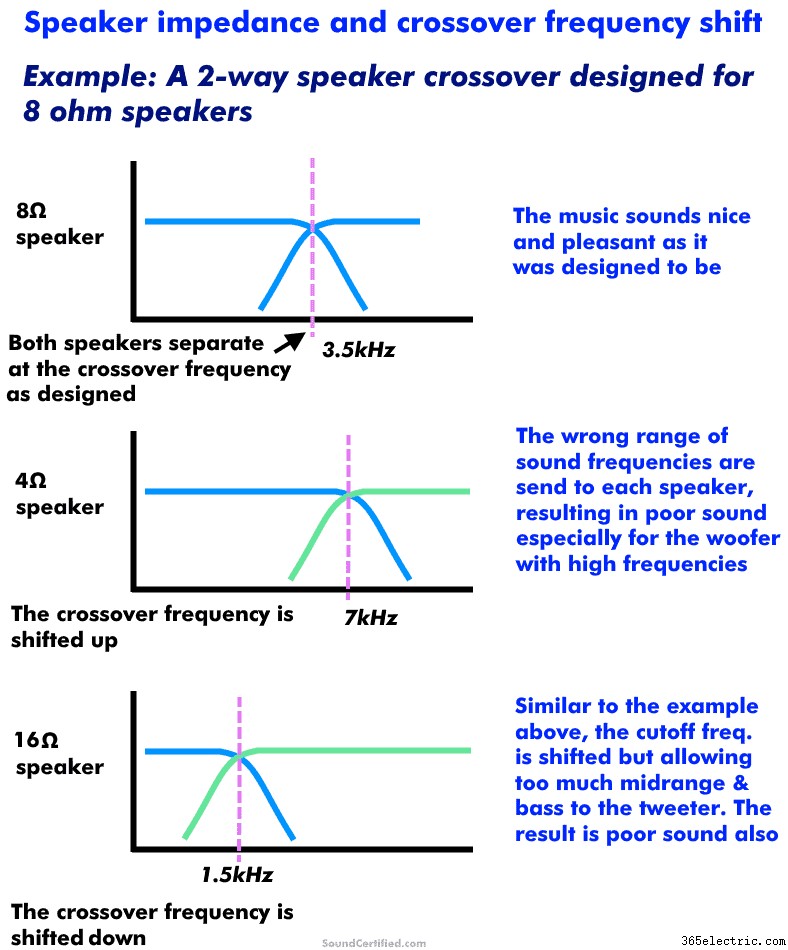
When you change the speaker impedance connected to a speaker crossover it can significantly shift the crossover’s cutoff frequency. As a general rule:
- Halving the speaker impedance (ex.:8ohms to 4 ohms) doubles the frequency
- Doubling the speaker impedance (ex:8 ohms to 16 ohms) halves the frequency
That’s bad because it allows the speakers to be sent a sound range they’re not suited for. In the case of tweeters, bass &midrange are bad because they can’t produce it properly. Similarly, many woofers can’t produce high frequency sounds well.
The end result in either case is poor sound that’s a lot worse sounding that it should be. If you change the speaker Ohms load you’ll have to replace the speaker crossover as you’ll need different parts values for it to work the same.
Is 8 or 4 ohm better? Is higher or lower impedance better for speakers?

8, 4, and 2 ohm speakers aren’t necessarily “better” than one another. The correct answer is that it depends on the application and what stereo or amplifier is being used. The best impedance is the one that matches an amplifier or stereo’s impedance spec correctly.
By industry tradition, 8 ohms are used for home and some theater speakers. 4 ohm speakers are generally used for car and marine audio, with some 2 ohm models also (usually subwoofers).
Például:
- 8 ohm speakers are used in home stereo systems and require 1/2 the current of a 4 ohm speaker. That means they can use smaller speaker wire as they can take advantage of home electrical systems that have a high voltage supply for driving speaker amplifiers.
- 4 ohm speakers are used because car stereos and amplifiers (particularly car head units) can’t make large amounts of power in speakers as they have a very low 12V power supply. Reducing the speaker impedance from 8 to 4 means we can double the power for the same output voltage.
As a matter of fact, car stereos can only put out about a small 15-18 watts RMS per channel, despite the exaggerated peak power ratings you may see in advertisements. That’s because they only have about 12 volts to work with and have to divide that in half in order to produce AC waves that drive a speaker.
Car amplifiers are able to deliver huge amounts of power to 4 and 2 ohm speakers. They use an internal “inverter” power supply that steps up the +12V supply to higher voltages. This way they’re able to supply much more power to 2 or 4 ohm speakers than would be possible otherwise.
More great articles to see
Did you enjoy my article? There’s plenty more where that came from!
- Did you know? You can power a car amp in your home.
- Want to learn more about audio? Find out here how speakers work.
- Tweeters are great but sometimes are too loud. In this guide I’ll show you how to reduce tweeter volume the right way.
Check out my full line of how-to &info articles here.
-
Az összefüggéseket a Resistance és hangszóró Noise
-
Mi a 6 Ohm Hangszóró ?
-
WikiPIT:kérdéseire válaszoltak
- Hogyan mérjük Hangszóró impedancia multiméterrel
- Hogyan is kiemelt impedancia hangszórók egy alacsony impedanciájú erősítő
- Hogyan állapítható meg, Hangszóró impedanciája
- Mi az autós hangszóró impedanciája? A hangszóró impedanciája és az ohmok magyarázata
- Miért káros a túl sok hűtőközeg a légkondicionálóra?
