Televíziós terminológiák:Fontos tudnivalók
Előfordult már veled, hogy beszélsz valakivel a tévétechnológiáról, és megemlítenek egy olyan szót, amit nem ismersz, és összezavarodnak? Találkozott már olyan kifejezéssel, amelynek nincs sok értelme, miközben elolvasta a legjobb tévé megvásárlására vonatkozó útmutatót? Számos szóval vagy terminológiával találkozunk a tévé olvasása vagy megbeszélése közben. Különösen bosszantó, ha tévét kell vásárolnia, és túl sok ismeretlen terminológiával kell szembenéznie. A probléma megoldása és az ismeretlen kifejezések megismertetése érdekében összeállítottunk egy listát a televíziós terminológiákról.
Itt megvitatjuk és megpróbáljuk egyszerű szavakkal elmagyarázni ezeket a nehéz terminológiákat.
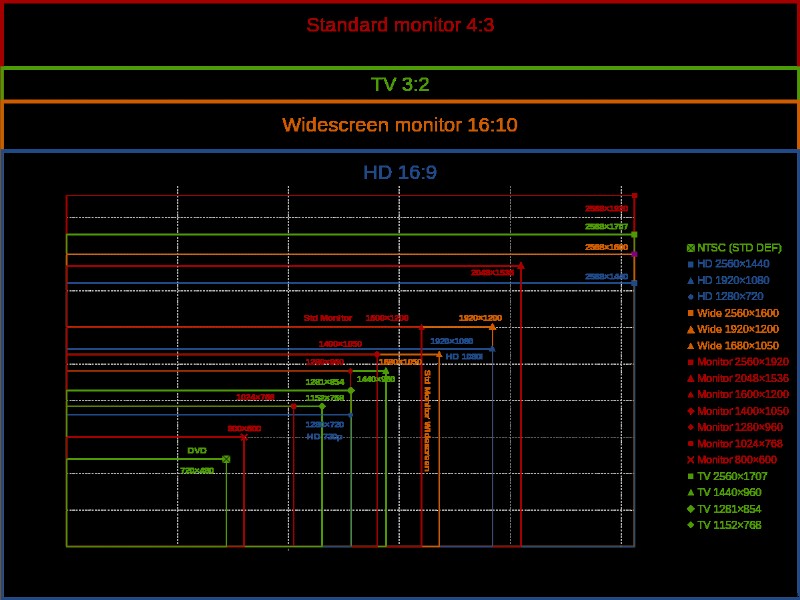
- Képarány:
A képarány a TV-képernyő szélességének és magasságának arányára utal, és meghatározza a TV alakját. Különféle képarányok léteznek a TV-k számára, és ez a felbontástól függően változik. Bizonyos képarányok csak bizonyos felbontásokhoz alkalmasak, és úgy vannak kialakítva, hogy a legjobb képminőséget nyújtsák torzítás vagy nyúlás nélkül, és megakadályozzák az üres helyeket a kép bármely oldalán. A tévéknél manapság a leggyakoribb képarány a 16:9. Ha a TV-készülék tartalma és képaránya nem egyezik, fekete sávok jelennek meg az üres területen (a függőleges sávokat oszlopládáknak, a vízszintes sávokat levélszekrényeknek nevezzük). Egyes TV-készülékeknél ez a probléma a kép nagyításával, a kép kivágásával vagy a kettő kombinációjával oldható meg.
A kép forrása:Wikimedia Commons - Keret:
Leegyszerűsítve az előlap a képernyő körüli keretet vagy azt a szerkezeti formát jelenti, amely a TV-készülék előlapján látható, a képernyő kivételével. Bár fontosak a szerkezeti integritás szempontjából, befolyásolják a megtekintési élményt, mivel minden oldalról lefedik a képernyő egy részét. A legtöbb tévé manapság előlap nélküli, ami nagyon vékony keretet jelent a képernyőn, ami lehetővé teszi, hogy a TV képernyője nagyobb legyen anélkül, hogy növelni kellene a TV méretét.

Kép jóváírása:trustedreviews.com - Kontrasztarány:
A TV kontrasztaránya a legvilágosabb és legsötétebb beállítás közötti arányt jelenti. A TV kontrasztaránya az egyik fontos jellemző, amely segít eldönteni, hogy a TV mennyire jó. Ez befolyásolja a képernyőn látható képeket, és a kontrasztarányt számos tényező befolyásolja, például a képernyő visszaverődése, a helyiség megvilágítása, a képbeállítások és maga a megjelenített tartalom. A TV kontrasztaránya két alapon mérhető, azaz a natív és a dinamikus kontrasztarányon. A natív kontrasztarány, más néven statikus vagy képernyőn megjelenő kontrasztarány, a TV-panel szerepét képviseli, míg a dinamikus kontrasztarány a jobb kontraszt érdekében a képernyő hátuljára szerelt LED-es háttérvilágítás ingadozását jelenti. A tévégyártók különböző módszereket alkalmaznak a kontrasztarány mérésére, így ez a funkció irreleváns az új TV vásárlásakor. De a kontrasztarány nagyon hasznos a különböző tévék összehasonlításakor, mielőtt eldönti, melyiket válassza.
- CRT:
A CRT vagy Cathode Ray Tube (más néven képcső) a CRT TV-ben egy vákuumcső, ahol a TV-n látható képek jönnek létre. A foszforral bevont vagy fluoreszkáló képernyőt elektronsugarak pásztázzák a képek létrehozásához. A sugarak előre-hátra mozognak, megvilágítják az üvegcső belsejében lévő foszforpontok vonalait, több vonalat húznak a képernyőn, és képeket vagy képeket hoznak létre a tévé számára. A már elavult Direct TV-kben egy nagy képcső volt, míg a hátsó és elülső vetítős CRT TV-kben három képcső található az elsődleges színekhez, azaz a zöldhez, piroshoz és kékhez.
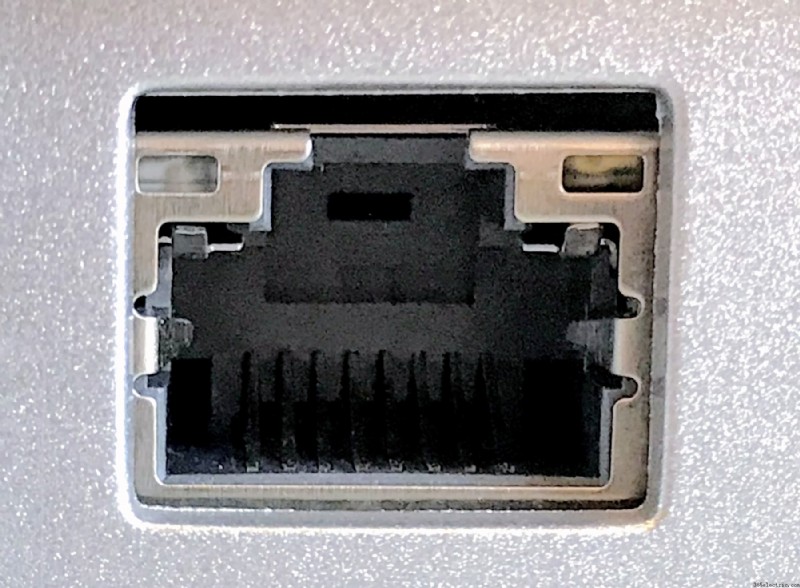
- Ethernet port :
A TV ethernet portja lehetővé teszi, hogy kábel segítségével csatlakoztassa tévéjét az internethez. Mindössze annyit kell tennie, hogy csatlakoztatja az Ethernet-kábel egyik végét a porthoz, a másik végét pedig az útválasztóhoz, hogy internetes műsorokat és filmeket sugározhasson a tévén. Stabilabb kapcsolatot biztosít alacsonyabb késleltetéssel és jobb sebességgel.
A kép forrása:Wikimedia Commons - Frame rate:
Frame rate means the speed at which the consecutive image slides are displayed. It is usually expressed as frames per second or fps. Higher the frame rate, the higher the number of frames used and it will mean more bandwidth for streaming the video. High frame rates have become popular these days as they capture a higher number of images per second which results in a smoother video. The high-definition videos often have a frame rate of 60 fps.
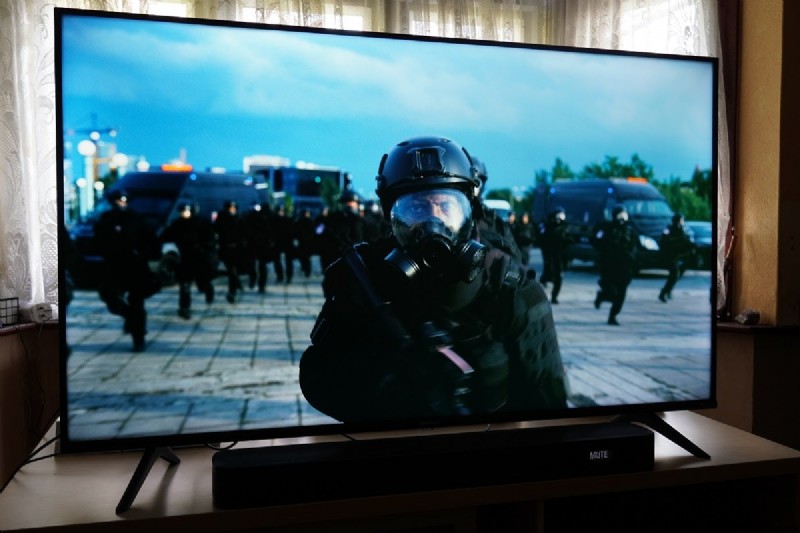
- HDMI:
HDMI or High-Definition Multimedia Interface is a digital interface that helps in transferring high-definition audio and video signals through a cable. It can be used to transfer a video quality of up to 4k Ultra HD resolution, 3D videos, and multichannel surround sound in high quality.

Image credit:Pixabay - HDR:
HDR or High Dynamic Range is a feature that affects the TV’s contrast ratio and color accuracy and helps make the pictures look more realistic. It is almost a must-have feature for TVs these days due to the detail it provides to the images through the right color balancing. Almost all the mid-range to high-range TVs have this feature and even most of the movies and shows on TVs are HDR now. Though, one thing to remember here is that TV HDR and photo HDR are not the same. These are two different concepts with the same name, making almost everyone confused.
- kHz:
KiloHertz or kHz represents a thousand frequency cycles per second. In simple words, it is a measurement of frequency i.e., the number of times a wave repeats itself in a second. 1 kHz means 1000 times per second. It is also used to measure the signal bandwidth, digital as well as analog. In the case of TVs, higher kHz means better sound quality.
- OLED:
OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) is a display technology that uses thin organic films between the two electrodes to produce light with the help of electricity. The organic process of creating the images on the screen with the light produced is called electroluminescence, meaning that the display is self-illuminating and does not need any backlight. OLED TV panels are lighter and thinner in comparison to LCD TVs and also help in saving energy.
- Over the top services:
Over-the-top services or OTT services are streaming services that offer media content directly to the viewers through the internet. These services are provided by bypassing the traditional platforms like broadcast, cable, and satellite TV. OTT content mostly includes shows and movies that you watch on phone, tablet, or laptop and can be streamed on an internet-connected TV like Smart TV. Some of the OTT service providers are Netflix, Amazon Prime, Disney+, etc.
- Pixelation:
Pixelation means stretching of the pixels beyond their original size and it is usually caused due to a weak signal. When the signal is poor, sometimes the TV fails to get the complete data or any data at all during the transmission. This leads to the formation of an incomplete image where some pixels are either missing or too stretched.
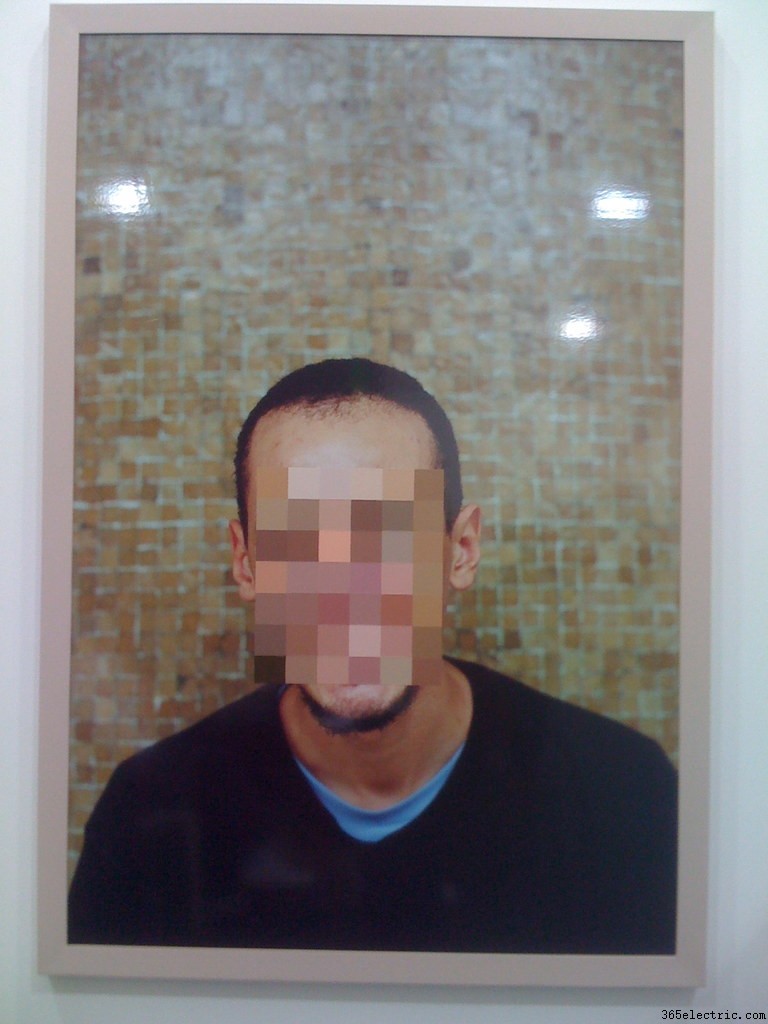

Image credit:Flickr - Plasma:
Plasma is a screen technology that was used in making the first flat display panels for large TVs and was a dominant TV technology just a few years back. A plasma display panel has small cells (like tiny CFLs) which are coated with red, green, or blue phosphorus. The cells also have neon or xenon gas inside them which creates invisible ultraviolet lights. These lights are then converted into the red, green, or blue light that we see on the screen via the light emitted by these cells. When we compare plasma with LEDs, plasma TVs are better as they have better picture quality and viewing angles. But, it also has many disadvantages, one of them being that it is now outdated technology. Also, the little cells or gas packets behind the panels can cause burn-in on your screen i.e. burn the images in your screen to show them even when your TV is switched off. They are also available only in larger sizes and are not that energy-efficient.
- Quantum Dots:
Quantum dots can be defined as nanocrystals that absorb light and convert its wavelength. These are used in QLED TVs where they are placed in front of a normal LED backlight in a layer. All these crystals emit individual colors of their own based on their size. Though the light emitted by these quantum dots still goes through the filter, the lights are highly pure that helps in expanding the TV’s color range, and creates more intense and deeper colors. These dots also enhance the light efficiency of the TV and thus produce brighter pictures.
- Resolution:
Resolution can be defined as the number of pixels or dots that create the pictures that you see on your TV screen. It is denoted as the number of pixels in one horizontal line by the number of pixels present in one vertical line. Higher the number of pixels, the higher the resolution, and the better the picture quality. There are four resolutions commonly used in TVs these days and each of them has a name as which are 1280×780 (HD), 1920×1080 (Full HD), 3840×2160 (Ultra HD/4k), and 7620×4380 (Ultra HD/8k). TV resolution is usually indicated in two ways, for example, 1080i or 1080p resolution. When you have both the options in front of you, choose the latter one. The “i” means interlaced and the “p” means progressive. The difference between both is that the interlaced videos display every alternate horizontal pixel line while the progressive lines display every horizontal pixel line, making the picture quality of progressive videos better than its counterpart.
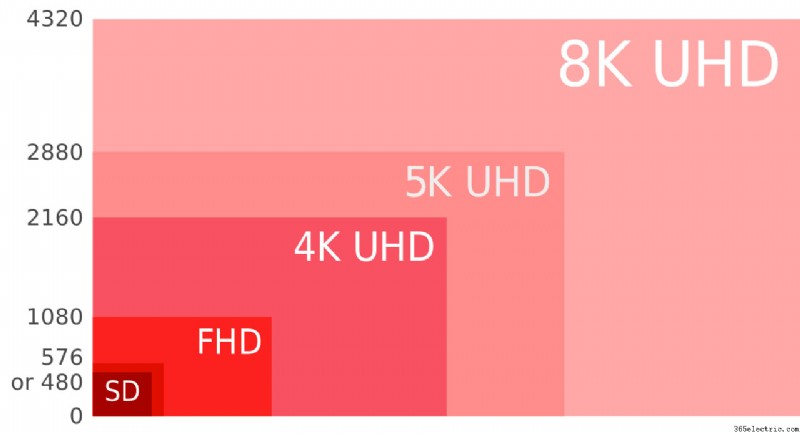
Image credit:Wikimedia Commons - Refresh Rate:
Refresh rate is defined as the number of times your TV screen refreshes itself in a second. It is denoted by Hertz or Hz. A higher refresh rate usually means smoother motion on the screen, but not always. However, the refresh rate should not be confused with the frame rate (fps). Frame rate represents the number of frames displayed on the screen per second. For clear motion and images, make sure that the refresh rate and frame rate of your TV match or in other words are the same, for example, if the refresh rate is 60 Hz, the frame rate should be 60 fps.
- Soap Opera Effect:
Soap Opera Effect is a visual effect created by most of the TVs by default. It involves creating additional frames in between the already existing ones by motion interpolation process to make the pictures look more crisp and realistic. It shows the content on your screen at a refresh rate that is higher than the original source of the content. Though it comes in handy when there is an action scene on the screen like sports events, it also wipes the normal cinematic blur from any fast-moving object on the screen. Removal of the blur hinders the ideal cinematic experience and makes the pictures more animated, giving them a soap opera effect, that is why the name. You can turn it off on your TV from the settings. This visual effect is also known as Enhanced Motion, Smooth Motion, or Auto Motion Plus, which are just marketing strategies.
- Viewing Angle:
Viewing angle means the maximum angle at which you can watch your TV screen comfortably without any color shift or loss of brightness. The ideal position is directly in front of the TV screen and at eye level. As per LCD/ LED TV manufacturers, the best viewing angle for your TV is 88 or more. At this angle, you get clear and well-defined images with the best color accuracy.
- UHD:
UHD or Ultra High Definition represents a higher resolution for the TV display. UHD TVs come in 4k (3840×2160) and 8k (7620×4380). These resolutions have a higher number of pixels than a normal HD TV. UHD displays are used in larger TVs, so you can enjoy a clearer and crisp image even while sitting relatively closer to the TV.
- Upscaling:
Upscaling basically means stretching an image with a lower resolution to fit on a larger display. In this, the pixels of the image with low resolution are copied and are repeated to fill up the display of a higher resolution. Almost every TV comes with upscaling now. In the case of HD TVs, the upscaling process makes the lower resolution images look bigger and better on the screen by increasing the pixel count.
